Table of Contents
Branching, tagging, and merging are concepts common to almost all version control systems. If you're not familiar with these ideas, we provide a good introduction in this chapter. If you are familiar, then hopefully you'll find it interesting to see how Subversion implements these ideas.
Branching is a fundamental part of version control. If you're going to allow Subversion to manage your data, then this is a feature you'll eventually come to depend on. This chapter assumes that you're already familiar with Subversion's basic concepts (Chapter 2, Basic Concepts).
Suppose it's your job to maintain a document for a division in your company, a handbook of some sort. One day a different division asks you for the same handbook, but with a few parts 'tweaked' for them, since they do things slightly differently.
What do you do in this situation? You do the obvious thing: you make a second copy of your document, and begin maintaining the two copies separately. As each department asks you to make small changes, you incorporate them into one copy or the other.
You often want to make the same change to both copies. For example, if you discover a typo in the first copy, it's very likely that the same typo exists in the second copy. The two documents are almost the same, after all; they only differ in small, specific ways.
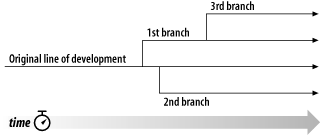
This is the basic concept of a branch—namely, a line of development that exists independently of another line, yet still shares a common history if you look far enough back in time. A branch always begins life as a copy of something, and moves on from there, generating its own history (see Figure 4.1, “Branches of development”).
Subversion has commands to help you maintain parallel branches of your files and directories. It allows you to create branches by copying your data, and remembers that the copies are related to one another. It also helps you duplicate changes from one branch to another. Finally, it can make portions of your working copy reflect different branches, so that you can “mix and match” different lines of development in your daily work.